Phone:
+6011-56331685
Email Address:
theneurofit@gmail.com

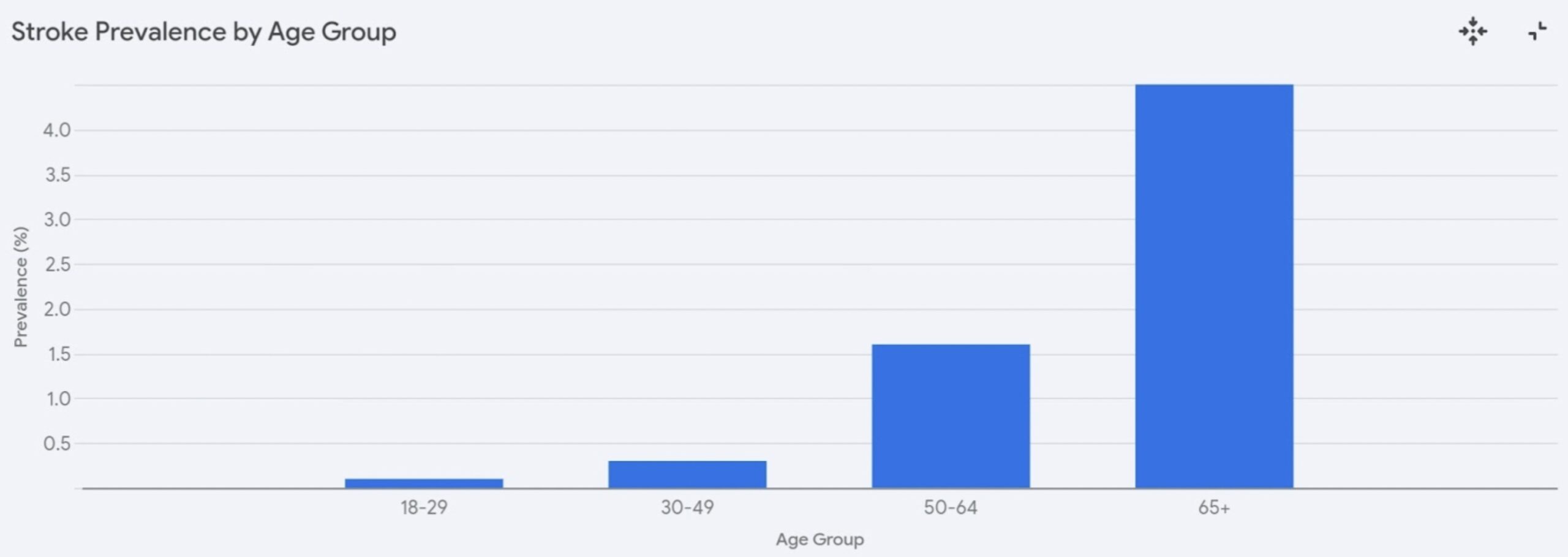
Stroke is a major public health concern in Malaysia, contributing to high rates of disability and death. According to the National Health and Morbidity Survey (NHMS) 2019, approximately 0.7% of Malaysians aged 18 and above have experienced a stroke. The risk increases significantly with age:
• Ages 18–29: 0.1%
• Ages 30–49: 0.3%
• Ages 50–64: 1.6%
• Ages 65 and above: 4.5%
The incidence rate of stroke in Malaysia is estimated at 150–180 cases per 100,000 people per year. Males are at a higher risk, with about 200 cases per 100,000, compared to 150 per 100,000 among females.
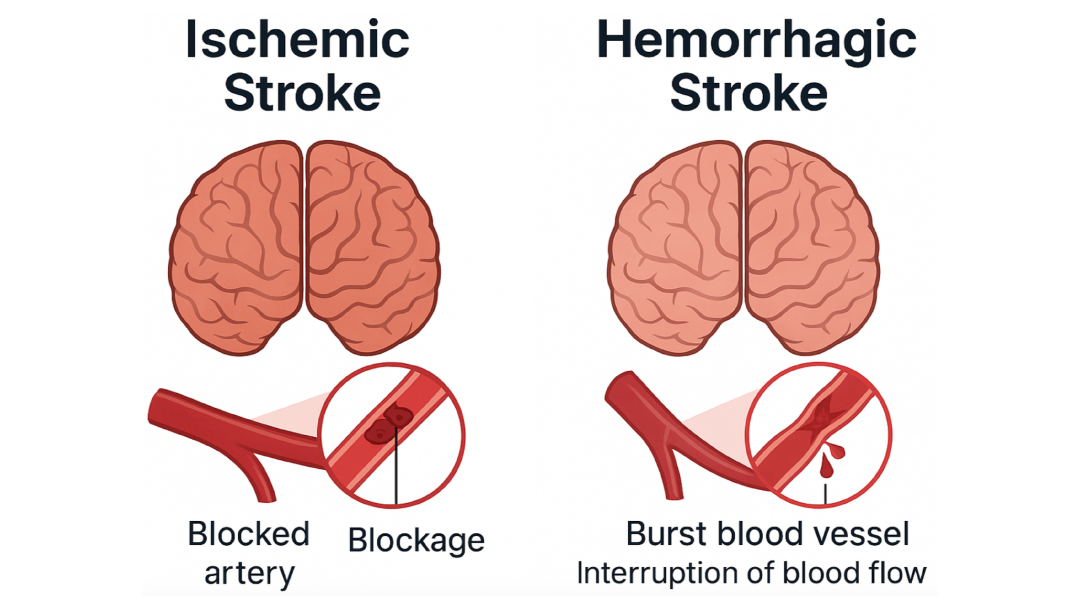
A stroke occurs when blood flow to a part of the brain is interrupted or reduced. Without oxygen and nutrients, brain cells begin to die within minutes, leading to brain injury.
There are two main types of stroke:
• Ischemic Stroke: Caused by a blockage in an artery leading to the brain (most common).
• Hemorrhagic Stroke: Caused by a burst blood vessel within the brain.
Understanding the risk factors can help prevent strokes or detect them early. Common causes include:
• Hypertension (high blood pressure)
• Diabetes Mellitus
• Hyperlipidemia (high cholesterol)
• Family history of stroke
• Obesity
• Lifestyle factors:
◦ Smoking
◦ Physical inactivity
◦ Excessive alcohol use
◦ Chronic stress
◦ An unhealthy diet
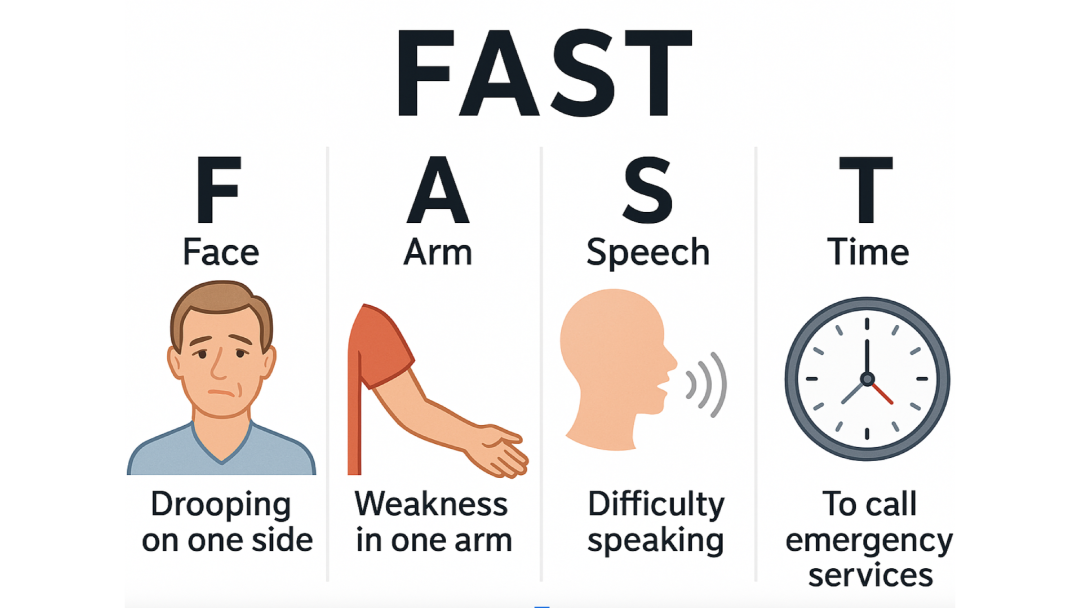
Time is critical in stroke management. Use the F.A.S.T acronym to identify stroke symptoms quickly:
• Face drooping
• Arm weakness
• Speech difficulty
• Time to call emergency services
Stroke rehabilitation is highly individualized and may include:
• Physical Therapy: To improve strength, movement, and balance—supporting activities such as bed mobility, walking, and transfers.
• Occupational Therapy: To help regain independence in daily tasks such as dressing and eating.
• Speech Therapy: For difficulties with speaking, swallowing, or understanding language.
• Psychological Support: Managing emotional challenges like anxiety, depression, or frustration is a vital part of recovery.
A stroke can be life-changing, but early treatment and structured rehabilitation can lead to meaningful recovery. Awareness, quick action, and ongoing support make a significant difference on the road to regaining independence and quality of life.